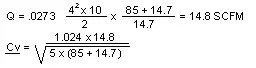Air Valve Sizing
Valve Sizing With Cv = 1 Table
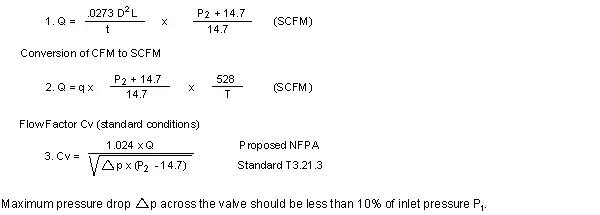
This method can be used if the required air flow is known or has been calculated with the formulas as shown below:
Air Flow Q (SCFM) for Cv = 1
Example 2: Find Cv if air flow Q (SCFM) is given.
![]()
low through valve from Table 28 for Cv = 1:30 SCFM
Cv = Air Flow Q (SCFM)
Air Flow at Cv = 1 (SCFM)
Cv = 60 SCFM
30 = 2.0
A valve with a Cv of minimum 2 should be selected.
Example 3: Find Cv if air flow Q (SCFM) to atmosphere is given.
Primary Pressure P1 = 90 PSIG
Air Flow to atmosphere Q = 100 SCFM
Flow to atmosphere through valve from Table 28 for Cv = 1:51 SCFM
Cv = Air Flow to atmosphere Q (SCFM)
Air Flow to Atmosphere at Cv = 1 (SCFM)
Cv = 100
51
Flow given is equivalent to valve with Cv = 2. This conversion is often necessary to size a valve properly, since some manufacturers do not show the standard Cv to allow a comparison.
| Inlet | Air Flow Q | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure | (SCFM) To | SCFM) To | ||||
| (PSIG) | 2 PSID | 5 PSID | 10 PSID | 15 PSID | 20 PSID | Atmosphere |
| 10 | 6.7 | 12 | ||||
| 20 | 7.9 | 11.9 | 16.9 | |||
| 30 | 9 | 13.8 | 18.2 | 21.8 | ||
| 40 | 9.9 | 15.4 | 20.6 | 23.8 | 26.6 | |
| 50 | 10.8 | 16.9 | 22.8 | 26.7 | 29.2 | 31.5 |
| 60 | 11.6 | 18.2 | 24.8 | 29.2 | 32.3 | 36.4 |
| 70 | 12.3 | 19.5 | 26.7 | 31.6 | 35.1 | 41.2 |
| 80 | 13 | 20.7 | 28.4 | 33.8 | 37.7 | 46.1 |
| 90 | 13.7 | 21.8 | 30 | 35.8 | 40.2 | 51 |
| 100 | 14.4 | 22.9 | 31.6 | 37.8 | 42.5 | 55.9 |
| 110 | 15 | 23.9 | 33.1 | 39.6 | 44.7 | 60.7 |
| 120 | 15.6 | 24.9 | 34.5 | 41.4 | 46.8 | 65.6 |
| 130 | 16.1 | 25.8 | 35.8 | 43.1 | 48.8 | 70.5 |
| 140 | 16.7 | 26.7 | 37.1 | 44.7 | 50.7 | 75.3 |
| 150 | 17.2 | 27.6 | 38.4 | 46.3 | 52.5 | 80.2 |
| 160 | 17.7 | 28.4 | 39.6 | 47.8 | 54.3 | 85.1 |
| 170 | 18.2 | 29.3 | 40.8 | 49.3 | 56 | 90 |
| 180 | 18.7 | 30.1 | 42 | 50.7 | 57.7 | 94.8 |
| 190 | 19.2 | 30.9 | 43.1 | 52.1 | 59.4 | 99.7 |
| 200 | 19.6 | 31.6 | 44.2 | 53.4 | 60.9 | 104.6 |
| 210 | 20.1 | 32.4 | 45.2 | 54.8 | 62.5 | 109.4 |
| 220 | 20.5 | 33.1 | 46.3 | 56.1 | 64 | 114.3 |
| 230 | 21 | 33.8 | 47.3 | 57.3 | 65.5 | 119.2 |
| 240 | 21.4 | 34.5 | 48.3 | 58.6 | 66.9 | 124 |
| 250 | 21.8 | 35.2 | 49.3 | 59.8 | 68.3 | 128.9 |
Example 1:
Find an air flow Q(SCFM) if Cv is known.
Cv = 1.8
![]()
Flow through valve from Table 28 for Cv = 1:21.8 SCFM
Q = Cv of valve x air flow at Cv = 1 (SCFM)
Q = 1.8 x 21.8 = 39.2 SCFM<
Example 4:
Find Cv if cylinder size and stroke speed is known, using formulas 1 and 3.
Primary Pressure = 90 PSIG
Pressure Drop across valve = 5 PSID
Cylinder Size 4″ Diam. x 10″ Stroke
Time to complete stroke 2 sec.